Retroperitoneal fibrosis
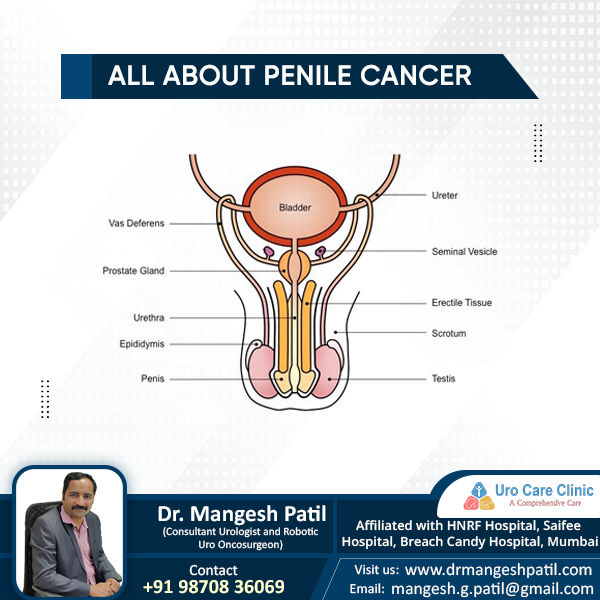
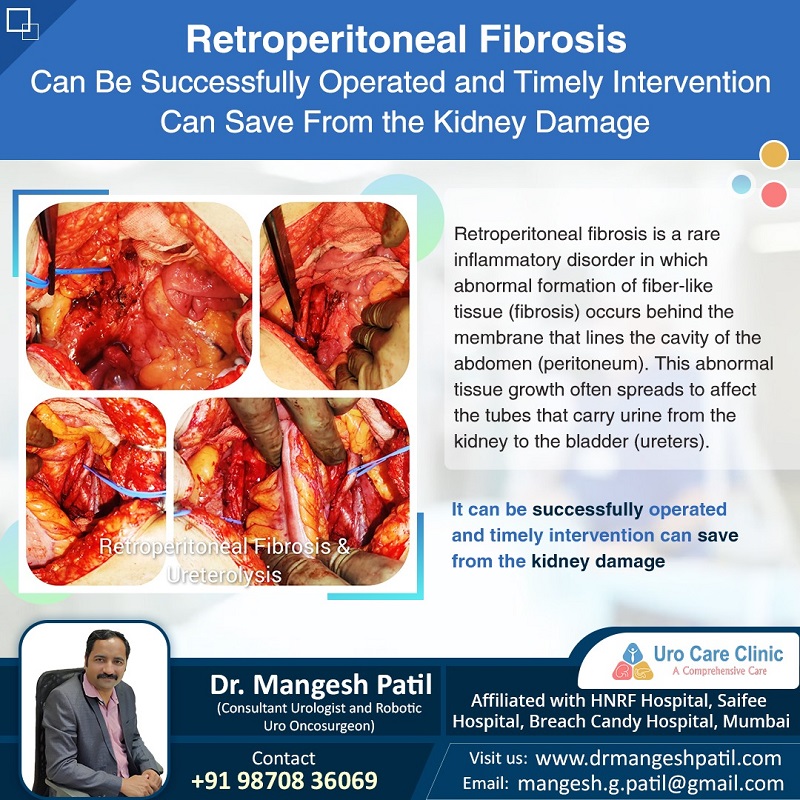
Retroperitoneal fibrosis also known as a Ormond’s disease is a rare condition that occurs when excess fibrous tissue develops in the retroperitoneal area (space behind stomach and intestine) which It causes a mass to form. This often causes compression and blockage of the ureters, which are the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder. Hence urine comes back to ureters. Urine backs up in the ureters can build up harmful materials in blood, and kidney damage can result. Retroperitoneal fibrosis, if left untreated, can cause kidney failure if it isn’t treated.
What are symptoms of retroperitoneal fibrosis?
Fibrosis causes decreased blood flow from the aorta to the lower part of your body. Early stage symptoms of fibrosis include:
- dull pain in the abdomen or back that may be hard to pinpoint
- pain on one side between your upper abdomen and back
- leg pain
- discoloration in one or both legs
- swelling of one leg
- intense abdominal pain with bleeding or hemorrhaging
Other symptoms include:
- severe abdominal or back pain
- appetite loss
- weight loss
- fever
- nausea or vomiting
- an inability to urinate
- reduced urine production
- impaired limb movement
- an inability to think clearly
- a low level of red blood cells, which is called anemia
- kidney failure
If you see these symptoms, contact best urology doctor near you
What are causes and risk factors of retroperitoneal fibrosis?
Risk factors of retroperitoneal fibrosis include:
- smoking
- exposure to asbestos
- tuberculosis
- actinomycosis, which is a bacterial infection
- histoplasmosis, which is a fungal infection
- recent trauma of the abdomen or pelvis
- abdominal or pelvic tumors
The disorder can also be associated with:
- recent surgery on the abdomen or pelvis
- the use of cancer treatments involving external beam radiation
- certain medications to treat migraines and high blood pressure
What procedure is used to diagnose fibrosis?
Your doctor may perform CT or MRI scans of your abdomen to diagnose the disease.
Other tests may be required to further diagnose the problem:
- blood tests to measure kidney function, anemia, and inflammation
- an X-ray of the kidneys and ureters, which is called an intravenous pyelogram
- an ultrasound of the kidneys
- a biopsy to check for cancer cells
What is treatment of retroperitoneal fibrosis?
Treatment of fibrosis depends on severity and location of the fibrosis. For early stage, your urology doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants.
In some cases, surgery may be required.
The goals of surgery is to remove the blockage, repair the affected ureter, and prevent it from happening again. For many people, treatment requires both medication and internal intervention.