Overview of Urological Cancers
Overview of urological cancers
Urologic cancers are the cancers that occur in the organs of the urinary tract and the male reproductive tract. It can affect organs like kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra, and in men the penis, prostate and testicles.
Types of urologic cancers:
Following are some types of urologic cancers
Bladder cancer:
Bladder cancer is one of the most common urological cancer. It occurs when bladder cells grow abnormally. It is more common in men than women. Bladder cancer is more common in older men who are age 60 or older.
Symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, pain or irritation, or frequent urination.
If you see these symptoms, visit a physician visit a urologist near you to determine a cause.
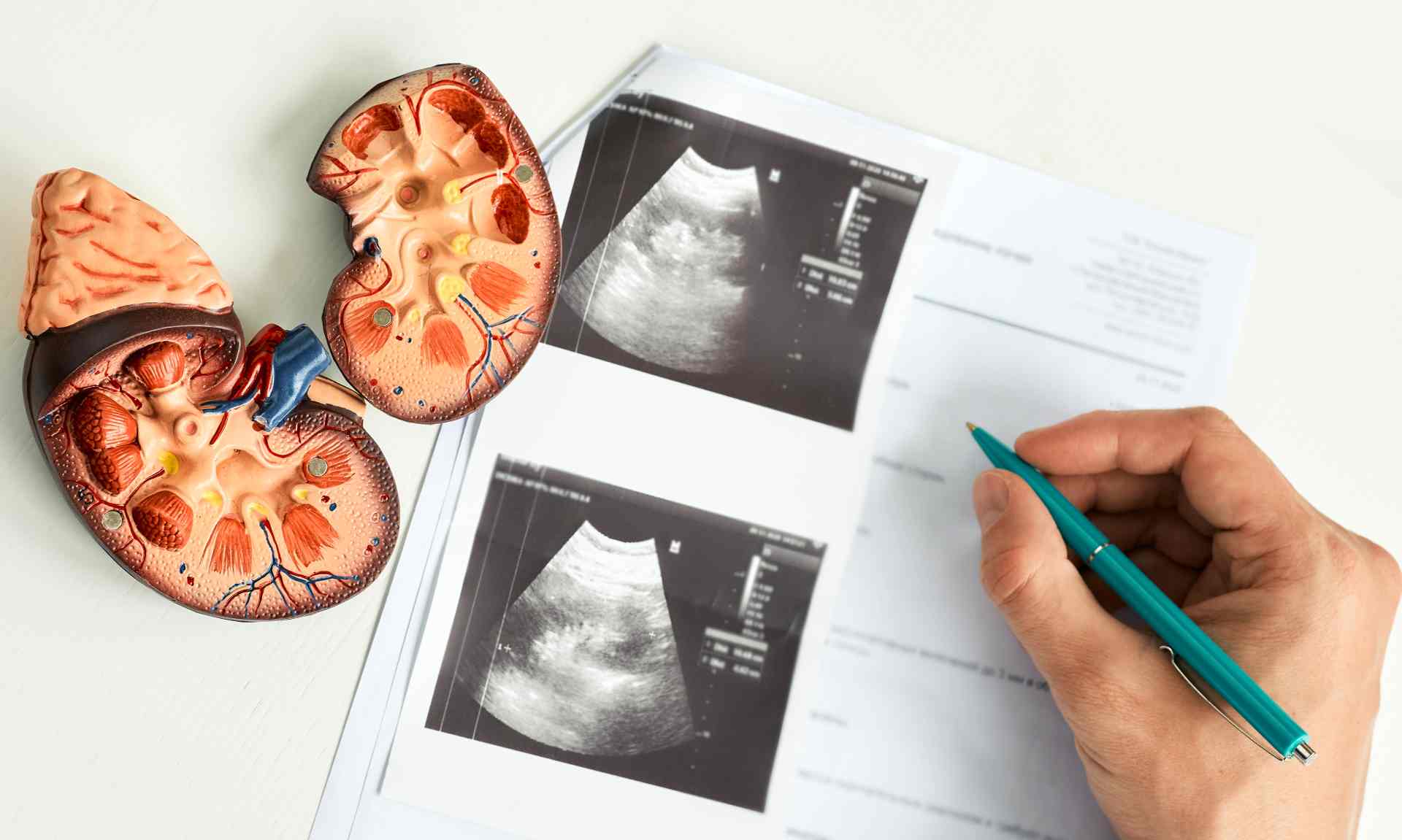
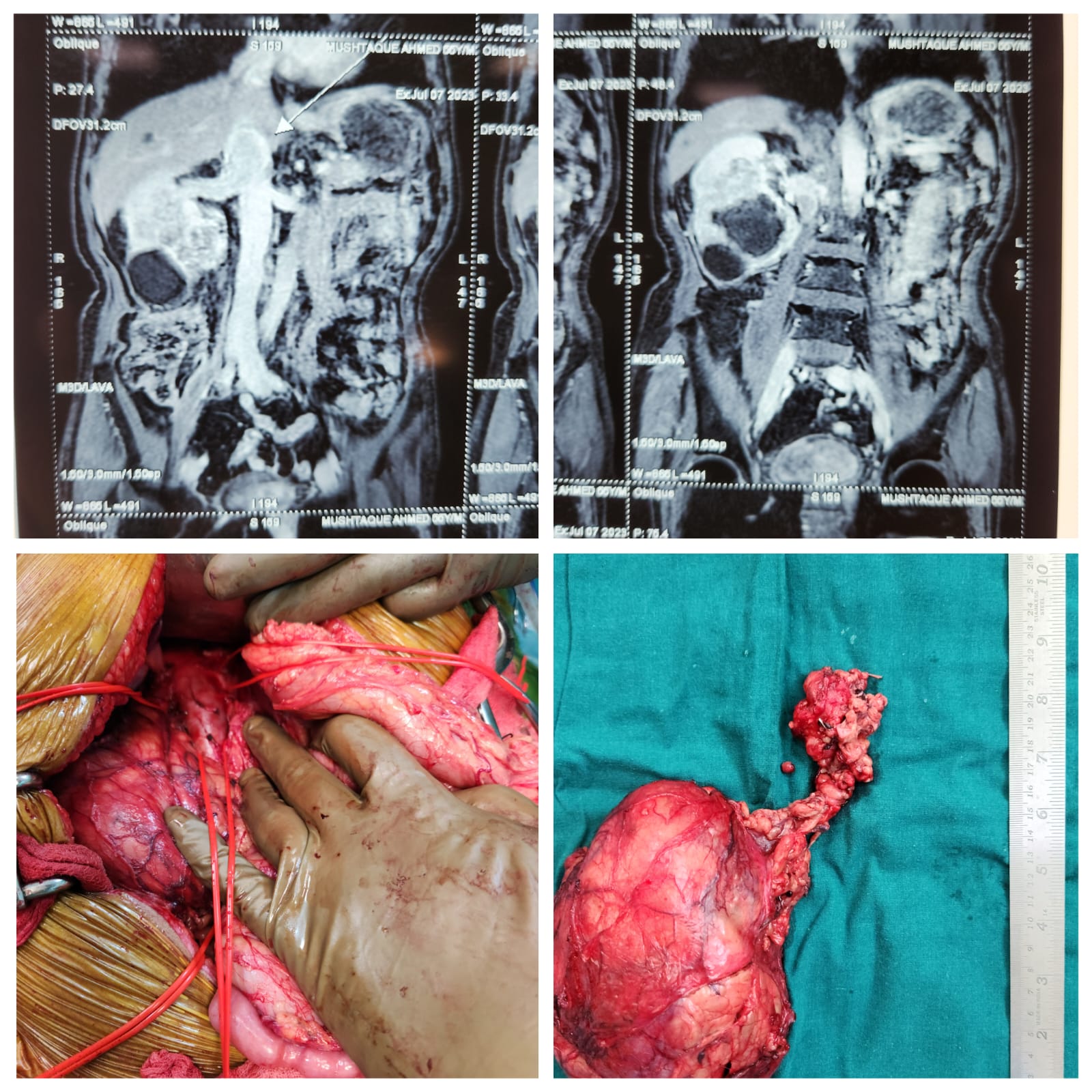
Kidney cancer
Kidney cancer occurs when cells of the kidney grow abnormally. Cancer cells may grow in the tissues or tubes within the kidney.
To read more about kidney cancer click here.
Penile cancer
It is rare urologic cancer that starts in the penis. It is usually a type of cancer cell called a squamous cell, which is a flat skin cell.
The cause of penile cancer is unknown. Men having HPV or AIDS are at higher risk, if they smoke, or if they have received certain treatments for the skin condition psoriasis.
Following symptoms can be seen in men with penile cancer:
• A blister or sore on the penis
• A wart-like growth that discharges watery pus
• Abnormal discharge from under the foreskin
• Bleeding
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate.
To read more about prostate cancer click here
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer occurs cells of the testis grows abnormally. It is rare and mostly occurs in young men. The symptoms of testicular cancer are a lump or swelling in the scrotum, and pain or a sense of heaviness in the scrotum, groin or lower belly. It can be detected by self-examination also. It usually occurs in only one testicle.
Testicular cancer mostly begins in the cells that make sperm. There are two main types of testicular cancers involving germ cells: seminomas and non-seminomas. Seminomas grow and spread slowly. Non-seminomas grow and spread faster.
It is highly curable, especially when physicians diagnose and treat it at an early stage.
Urethral cancer
Abnormal cells in the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body) cause urethral cancer. It is rare cancer and more common in older women and in people who have had bladder cancer. Its symptoms are similar to those of other urologic cancers like blood in urine, a stop-and-go stream of urine, pain in the groin or pelvis, or painful or frequent urination.
Treatment of urological cancers:
Surgery is mostly recommended by uro onco surgeons to treat most urologic cancers. The Tumour (the clump of abnormal cells) is removed surgically. For some conditions, physicians will recommend radiation therapy such as in place of or after surgery in which high-energy beams, like x-rays, are used to control or stop cancer cells from growing. In some cases, chemotherapy may be required to destroy cancer cells or control their growth.
For more information about urologic cancers and its treatment contact directly to Dr. Mangesh Patil. He is one of the most experienced uro onco surgeons in Mumbai. He uses most advanced treatment methods for cancer treatment for the maximal benefit of patients.